[ez-toc]
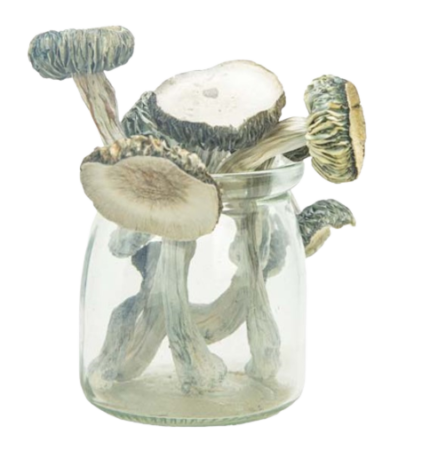
Amanita Muscaria Magic Mushrooms
Amanita Muscaria Mushroom commonly known as fly agaric mushroom, is a poisonous species of mushroom which grows in temperate climates across the world. It can be identified by its bright red cap with white spots, and is commonly found near birch trees. Amanita Muscaria Mushrooms have been used for many centuries in traditional medicine and folk remedies, particularly in Eastern Europe. It has been used to treat a variety of ailments, including fever, influenza and other illnesses.
It is can be a poisonous mushroom if eaten raw, but the toxins contained within it can be reduced through drying and boiling. It is also important to take care when handling the mushroom, as contact with its poisonous toxins can cause skin irritation and other adverse effects. When dried, Amanita Muscaria Mushroom can be brewed into a tea or used in capsules or tinctures. Its effects are said to range from sedative, calming and pain relief properties to hallucinogenic effects.
Amanita Muscaria, or the Fly Agaric mushroom, is a gilled fungus that has been of interest to biologists, mycologists, and cultural anthropologists for centuries. While its white gills, red cap and warty top have been iconic for decades, the universal veil that surrounds the mushroom has also been studied in-depth. This veil is an important part of the mushrooms development, and was first explored by gordon wasson in the late 1950s.
The ingestion of fly agaric amanita muscaria mushrooms has also been a subject of cultural fascination, with many societies from ancient times using its purported psychoactive properties in religious ceremonies and celebrations. In more recent centuries, the mushroom has been studied extensively for its potential medicinal applications in the treatment of a variety of conditions.
This mushroom is a psychoactive mushroom that has been used for centuries in spiritual, religious and medicinal practices. It is classified as an entheogen because it has the ability to cause profound alterations in consciousness due to its central nervous system activity. The psychoactive compounds in the Amanita Muscaria mushroom are muscimol and ibotenic acid.
When consumed, these compounds can produce psychoactive effects such as euphoria, sleepiness, increased appetite and even hallucinations. Over the centuries, there have been many reports of Amanita Muscaria use for spiritual and religious ceremonies as well as medicinal practices.
Amanita Muscaria mushrooms are a common sight in regions of the northern hemisphere, including North America. In the united states, Amanita Muscaria is most commonly found in dried mushroom form. These edible species occupy temperate and boreal regions, with a preference for coniferous and deciduous forests.
They can be found under trees such as spruces, pines, and firs, as well as birch. They are recognizable by their bright red caps with characteristic white spots that resemble a fly’s wings. Amanita Muscaria mushrooms can often be found in groups, since they are spread by mycelial networks.
Amanita Muscaria, commonly known as the fly agaric mushroom, is an easily recognizable species of amanita mushrooms. It is found in temperate regions of the Northern Hemisphere and is characterized by its red and white spotted cap.
Over time, this fungal fruiting body has become associated with folklore and myth, primarily due to its red and white colors resembling Santa Claus. In fact, amanita muscaria var. alba, a white variant of amanita muscaria, is often referred to as Santa’s Mushroom.
Amanita muscaria effects:
The effects of Amanita muscaria ingestion have been widely reported amongst various indigenous cultures. Effects range from psychoactive to medicinal, and have been studied in both animal and human experiments.
Common effects include changes in consciousness, enhanced emotions, sensations of euphoria, hallucinations and vivid dreams, and a profound sense of connectedness to the environment. Depending on the dose, some users have experienced extreme reactions such as nausea, vomiting, headaches, dizziness and visual disturbances.
Amanita muscaria has also been used traditionally by various cultures to treat many ailments, including headaches, nausea and gastrointestinal problems. It has been used to reduce pain and improve overall wellbeing. While there is limited scientific evidence to support these claims, some studies suggest that the mushroom could contain compounds that help improve overall health and reduce inflammation.
Beyond its medicinal uses, Amanita muscaria has also been used for spiritual purposes. In particular, some Native American cultures have incorporated the mushroom into religious rituals, where it is believed to help facilitate communication with the spirit world. More recently, some practitioners have also recommended using Amanita muscaria in ayahuasca-like ceremonies, where it is thought to enhance the effects of the traditional brew.
Regardless of its use, it is important to note that Amanita muscaria can be dangerous if taken in high doses. It is recommended that users start with a low dose and gradually increase it until the desired effects are achieved. Furthermore, it is important to obtain mushrooms from a reliable source and take them only in the presence of an experienced practitioner. By taking these precautions, Amanita muscaria can be a safe and beneficial addition to any health or spiritual journey.
Frequently Asked Questions:
a. are amanita muscaria mushrooms poisonous?
Yes, Amanita muscaria mushrooms are considered to be poisonous and must not be ingested. Symptoms of mushroom poisoning vary depending on the type of mushroom ingested, but can include abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting and diarrhea. In some cases, more serious effects such as liver damage may occur. If you suspect that you or someone else has ingested Amanita muscaria mushrooms, seek medical attention immediately. It is also important to note that Amanita muscaria mushrooms can be mistaken for other, non-poisonous mushrooms, so it is best to avoid picking and consuming mushrooms in the wild.
b. where do amanita muscaria mushrooms grow?
Amanita muscaria mushrooms typically grow in forests, meadows and other areas with ample moisture during the summer months. They can be found in many parts of the world, including Europe, Asia and North America. The mushrooms are most common in temperate climates with a humid climate, although they can be found in other regions as well.
c. what do amanita muscaria mushrooms look like?
Amanita muscaria mushrooms are recognizable by their bright red caps, white spots and thin, wavy stems. The cap of the mushroom is often convex or flat in shape and can range from a few inches to several feet in diameter. The cap may also be yellow or orange instead of red, depending on the region. The white spots are usually the remnants of a veil that covers the gills and stem. The stem is generally thin, hollow and smooth. When broken, the stem releases a white powder. Amanita muscaria mushrooms may also have volva at the base of their stems, which are remnants of the mushroom’s universal veil.
d. what is the history of amanita muscaria mushrooms?
Amanita muscaria mushrooms have a long and varied history. Ancient cultures such as the Greeks, Romans and Celts believed that these mushrooms had supernatural powers and used them in various rituals. In some regions, the mushrooms were consumed as part of religious ceremonies. Some accounts also suggest that the mushrooms may have been used to induce altered states of consciousness. In modern times, Amanita muscaria mushrooms are still consumed by some people, although this is generally not recommended due to their potential toxicity.
e. are amanita muscaria mushrooms hallucinogenic?
Amanita muscaria mushrooms contain a number of compounds which may have hallucinogenic effects. However, the extent to which these compounds produce hallucinations is disputed. Furthermore, due to the potential toxicity of Amanita muscaria mushrooms, it is not advised that they are consumed in order to achieve a hallucinogenic effect.
f. can amanita muscaria mushrooms be eaten?
No, Amanita muscaria mushrooms should not be eaten due to their potential toxicity. Symptoms of mushroom poisoning can range from abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting to more serious effects such as liver damage. If you suspect that you or someone else has ingested Amanita muscaria mushrooms, seek medical attention immediately. It is also important to note that Amanita muscaria mushrooms can be mistaken for other, non-poisonous mushrooms, so it is best to avoid picking and consuming mushrooms in the wild.













Reviews
There are no reviews yet.